SPLIT INCOME
Discover how you can make regular and consistent weekly income , whilst being totally hands off with your trading account.
POTENTIAL CAPITAL GROWTH AND CONSISTENT WEEKLY INCOME
- What is Share Trading01
- Key Features of Share Trading02
- Trade Both Long and Short03
- Calculating Profits and/or Losses04
- Share Trading Examples05
- Key Benefits of Shares06
- Margin Lending07
- Risks of Share Trading08
- Styles of Share Trading09
- Tools & Resources10
- How to Open an Account11
- Supported Brokers12
Split Income Strategy
Offering leveraged returns and total diversification, this is an opportunity for MTA to execute the Split Income strategy for you.
Our mission is to help our clients gain exposure to the stock market, without having to do any of the heavy lifting themselves. Best part – there are no joining fees and you can have the opportunity to have a professionally built strategy executed on your account.
1. Introducing the Split Income Strategy
This strategy lets you sell options on ETFs and collect a weekly options premium of about 0.5%-1.5% or more. We'll explain how to sell options and earn a weekly options premium throughout the year. The method involves selling put options on half your position while holding shares for the other half. When assigned on the sold put options, you own the shares and sell call options on half of your overall position, known as a Covered Call. We'll focus on using UPRO, a geared S&P500 ETF, which is good for this strategy because of its liquidity and volatility.
Selling puts is generally less risky and offers some protection against a drop in the asset’s price. This strategy is attractive because it lets you earn the option’s time value, which changes based on the option’s strike price, expiration date, and the asset’s volatility. For UPRO, with its current price, the average weekly income from selling at-the-money puts is about 0.5% to 1.5% or more.
Assuming a weekly income of 1.0%, if the market doesn’t change much over a year, this can lead to substantial income. While you need to be aware of potential losses from market declines, the income from options can significantly offset those losses.
If you’re interested in learning more about the “Split Income Strategy” and earning weekly income, keep reading below.
| Split Income | Details |
|---|---|
| Minimum Investment | US$15,000 |
| Market | UPRO |
| Strategy Type | Option Selling |
| Average Trade Length | 1 Week |
| Leverage | 3xLeveraged |
| Suggested Portfolio Allocation | <10% |
2. What is the UPRO ETF?
The UPRO ETF stands as a high-octane investment vehicle, engineered to amplify the daily performance of the S&P 500 by threefold, before accounting for fees and expenses. This leverage effect means that UPRO investors ride a wave that is thrice as steep, whether climbing or descending, compared to the benchmark index. The heightened volatility of UPRO is a double-edged sword, offering a pathway to magnified returns for those who opt for options trading or have a penchant for high-stakes play in the ever-fluctuating market landscape. It's an instrument that resonates with the investment strategy of those who are comfortable occupying the vanguard of risk, looking to leverage market movements to their advantage. Exploring the integration of UPRO into a diversified portfolio could open doors to substantial growth potential, with the caveat of increased exposure to market swings. Key Points:
KEY POINTS:
1
3x Daily Performance:
UPRO aims to deliver triple the daily returns of the S&P 500, magnifying both upward and downward movements.
2
Enhanced Options Trading:
The ETF is tailored for investors who utilize options trading to capitalize on its pronounced volatility.
3
Amplified Risk and Reward:
With great power comes increased risk; UPRO’s leverage means higher potential returns are coupled with heightened risks.
4
Volatility Consideration:
Its intrinsic volatility positions UPRO as an appropriate fit for the high-risk segment of an investment portfolio.
5
Strategic Portfolio Placement:
UPRO is best suited for investors seeking aggressive growth and who are comfortable with significant market exposure.
6
Investment Strategy Integration:
Incorporating UPRO into an investment strategy requires an appetite for risk but offers the potential for substantial rewards.
3. Strategic Considerations
MTA's Split Income Strategy serves as a compelling blueprint for investors aiming to harness the inherent volatility of leveraged ETFs like UPRO. By employing a dual approach of selling put options on half of one's position while holding shares for the other half, investors are positioned to collect weekly premiums. This strategy is particularly advantageous due to UPRO's liquidity and volatility, enabling the potential capture of 0.5% to 1.5% in weekly options premiums. While the promise of substantial income from options selling is enticing, investors must remain vigilant of the market's unpredictability and the heightened risks that come with a leveraged ETF, which could lead to significant income or conversely, considerable losses
Understanding the mechanics of the strategy is crucial; it isn’t merely a set-and-forget procedure but one that requires active management and strategic decision-making. Choosing between out-of-the-money, at-the-money, or in-the-money puts will significantly influence investment outcomes, and this selection process must adapt as the market ebbs and flows. In essence, the strategy’s flexibility to move the strike price up with the market or down when it falls underscores its dynamic nature, a necessary feature to navigate the turbulent waters of leveraged ETF investing.

However, the strategy’s prowess is truly tested during market downturns. While selling ATM options since 2015 has shown to be less volatile than holding UPRO outright, it is not immune to market sell-offs, which can result in substantial losses. Therefore, the Split Income Strategy underscores the importance of strategic adjustments after market dips, illustrating that a nuanced understanding of market volatility and its impact on option pricing is paramount. The process of earning premiums through put selling introduces a buffer against potential losses, emphasizing the strategy’s merit in balancing risk and reward in a volatile investment landscape.
4. How Does the Strategy Work?
Markets fluctuate constantly; they don’t simply move in a straight line or maintain a consistent pattern. This unpredictability means that accurately forecasting market movements is generally not feasible. Even during a strong upward trend, there will be periods of decline. Success in investing hinges on navigating these ups and downs effectively.
In this strategy, the approach to selling put options on half of the position—whether choosing out-of-the-money (OTM), at-the-money (ATM), or in-the-money (ITM)—plays a crucial role in the outcome of one’s investment efforts. Opting for ATM put selling involves either rolling the put to the current price upon expiration or acquiring the stock and selling ATM calls. This strategy adjusts with the market: you move the strike price up if the market rises and down if it falls.
However, this method is not without its challenges. For example, an analysis of selling ATM options on UPRO since 2015 shows that while this strategy tends to be less volatile than holding UPRO itself, it’s also vulnerable to significant losses during market downturns.
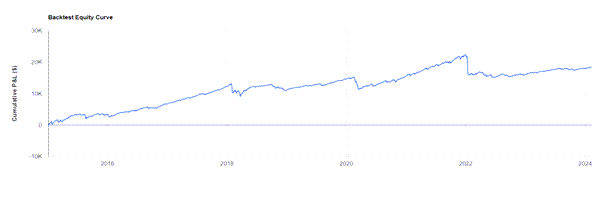
The strategy’s effectiveness often wavers due to market volatility, which can lead to rapid gains or losses in alternating market conditions. This “whip-saw” effect in fluctuating markets suggests that those investing in highly volatile instruments like UPRO might need to adjust their positions following market dips to mitigate risks.
Selling puts at the money (ATM) is more nuanced than it appears at first glance, encompassing not just the potential for profit but also the exposure to certain risks. Investors must adeptly manage the swings in market trends and volatility to optimise their returns.
Understanding put selling starts with the basics: by selling a put option, you earn a premium and agree to purchase the underlying asset at a set price should it drop below that level by the option’s expiration. If the asset’s price remains above this threshold, the option expires worthless, allowing you to retain the premium and possibly repeat the transaction. This mechanism highlights the importance of strategic decision-making in options trading, where market insights and risk management are key to sustaining profitability.
Let’s put this in simpler terms: Imagine you sell a put option and the market drops, pushing you to buy the stock at a price higher than its current market value. This situation might seem like a loss, but there is a way to manage this. Once you own the stock from your put option, you could sell calls that are out of the money (OTM) instead of selling them at the current price. Here’s why that’s smart:
- If the stock price keeps dropping, the premium you get from selling the call option helps reduce your loss a bit.
- If the stock’s price goes up, not only do you keep the premium from the call option, but you might also make some money from the stock going up to the price where you sold the call.
This way, you have a chance to make back some or all of your initial loss.
The equity for selling Delta 0.3 call options against your stock position when the market is declining is shown in the following graph:
The equity for selling In the Money options when the market is declining is shown below:
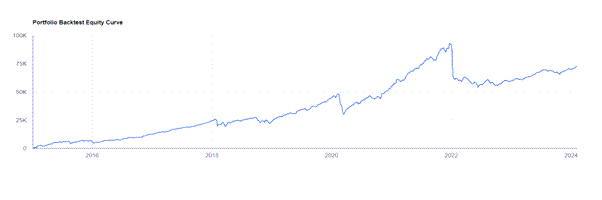
The “split income strategy” offers a better approach than just selling at-the-money (ATM) options on half your shares. When stock prices fall, this strategy avoids lowering the strike price for new options. Instead, it continues to sell options at higher strike prices until any losses on the stock are recovered. Then, it switches back to selling ATM options. This method might mean giving up some potential profit from the option’s extrinsic value (the part of the option’s price not directly linked to the stock’s current price) to prevent significant losses from rapid price changes. This way, the risk of losing money from the stock’s actual value is minimised.
Let’s run through some examples below assuming we sell put options or call options on half of the UPRO position, whilst always maintaining a stock position on half of your overall UPRO exposure:
5. Examples
The strategy consists of several rules for deciding when to buy (enter) or sell (exit) options. These rules are based on price movement in the underlying UPRO shares.
Scenario 1: Bullish Market
- The initial position starts with buying UPRO shares, for example 100 shares and then selling an ATM (At the Money) put option on the other half of the position, i.e. 1 contract in this example. The initial position therefore starts with 100 shares and 1 sold put option.
- Regarding the put option, let’s say you choose to sell a put option for UPRO that’s priced right where UPRO is trading, example $60, and UPRO’s current price is $59.95. You get $2 for each share from this deal. If UPRO’s price stays over $60 until the option’s end date, you get to keep the $2 per share as your profit, and the option doesn’t get exercised.
- If UPRO’s price falls below $60 and you end up owning the stock at $60, but you’ve already made $2 per share from the premium, your actual starting point, or breakeven, is $58 ($60 minus the $2 premium). So, you’re not losing money unless UPRO’s price drops below $58. At this point, it’s smarter to keep your strategy focused on a $60 strike price for selling a covered call, rather than lowering the strike price of your call option in response to market changes.
- If UPRO’s value decreases significantly, say by over 5%, instead of opting for a call option at a $60.00 strike price, choose to sell a call option that’s out of the money with a delta of 0.3. This strategy, involving a UPRO covered call, lets you earn extra premium, which could help recover some or all of your stock losses. You can keep this covered call until it expires. If it ends up being worthless, you then sell another call with a 0.3 delta and continue this process until UPRO’s price is back above your initial buy-in point.
- If your call option is assigned and you’ve returned to a cash position, check your account to decide your next move based on UPRO’s current price. If UPRO is now trading above $60, start selling at-the-money (ATM) puts. If it’s below $60, opt for selling a put that’s in the money (ITM), specifically one with a strike price above UPRO’s current price and a delta of 0.7. This approach aims to strategically re-enter the market based on the prevailing price conditions of UPRO.

Scenario 2: Sideways Market
- When the market doesn’t show a clear up or down trend, and UPRO’s price hovers around its current level, ending near the strike price of your sold put option, you should stick to selling at-the-money (ATM) puts on UPRO. If the closing price is higher, you pocket the premium from the put option and then proceed to sell another put option.
- Should UPRO’s price fall and you end up owning the stock, it’s smart to sell a call option at the same price you paid for the stock. Continue selling call options until one is executed, at which point you should switch back to selling put options.
Scenario 3: Bearish Market
- When the market takes a downturn and UPRO’s value falls below your put option’s strike price, leading to an assignment, you should avoid lowering your target by selling at decreased strike prices. Instead, maintain your original strike price level and opt for selling a covered call at that same price you were assigned at.
- If there’s a significant drop in price, aim to sell a covered call option that has a delta the closest to 0.3, which will be out of the money. This approach not only provides extra income but also aids in mitigating some of the financial setbacks.
- Should UPRO’s price continue to decline and your covered call ends up not being assigned (expires worthless), keep holding onto the stock. Proceed to sell another covered call, setting the strike price using a delta of 0.3, and repeat this process until you get assigned. Afterward, switch strategies by selling put options that are in the money with a delta of 0.7, until price is above the initial entry point at which you were assigned.

The Split Income Strategy emphasises that while no approach is entirely without risk, selling out of the money call options when in a stock position after being assigned on a sold put could help lessen losses and recoup intrinsic value, especially in an unpredictable market. This strategy benefits from increased volatility, as higher volatility often means higher option premiums than you’d see in a more stable market environment.
To sum up, the Split Income Strategy offers a balanced way to navigate markets that have both growth opportunities and the potential for loss. By staying disciplined and waiting for market rebounds, investors may recoup a large part of the loss in value experienced during downturns. This approach aims for long-term gains by occasionally foregoing extrinsic value to avoid the traps of highly volatile, or “whipsaw,” market movements.
To have this strategy executed for you on your trading account please select the ‘Sign Up Now” button below to proceed. On the next page you will be asked for your name, email and phone number. We will check to see if you have an existing account, if so we will send you our Strategy Execution Agreement. If not we will help you to open an account with Interactive Brokers, which will be linked to MTA so we are able to execute trade on your account once funded.
